IGRT
(Image Guided Radiotherapy)
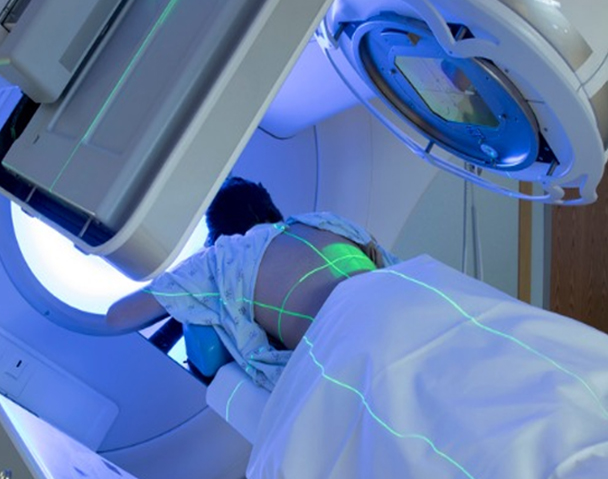
Image Guided Radiotherapy (IGRT) is an advanced technique used in radiation therapy to precisely target tumors while minimizing radiation exposure to surrounding healthy tissues. It involves the use of imaging technology to verify the position of the tumor immediately before or during each treatment session.
Here's how IGRT works:
Imaging Modalities: IGRT utilizes various imaging modalities such as X-rays, CT scans, MRI, or ultrasound to visualize the tumor and surrounding anatomy. These images provide detailed information about the size, shape, and location of the tumor, as well as nearby critical structures.
Patient Setup and Alignment: Before each treatment session, the patient undergoes imaging to ensure accurate positioning. The images obtained are compared to reference images taken during the treatment planning process. Any discrepancies in the tumor position or patient alignment are corrected to ensure precise targeting.
Adaptive Treatment Planning: Based on the imaging data acquired during each session, adjustments can be made to the treatment plan in real-time. This allows radiation oncologists to adapt the treatment to changes in tumor size, shape, or position, as well as variations in patient anatomy.
Motion Management: IGRT is particularly useful for managing tumor motion caused by factors such as breathing or organ movement. Techniques such as respiratory gating or tumor tracking can be employed to account for motion and ensure accurate delivery of radiation.
Verification and Quality Assurance: IGRT systems incorporate built-in verification tools to confirm that the treatment is delivered as planned. Quality assurance measures are implemented to verify the accuracy and consistency of the imaging and treatment processes.
Benefits of IGRT include
Increased Precision: IGRT enables highly accurate delivery of radiation, minimizing the risk of damage to healthy tissues and reducing potential side effects.
Improved Tumor Control: By ensuring precise targeting of the tumor, IGRT may enhance tumor control rates and treatment outcomes.
Reduced Toxicity: With IGRT, radiation oncologists can confidently escalate the radiation dose to the tumor while sparing nearby organs at risk, leading to reduced toxicity and improved patient tolerance.
Enhanced Safety: Real-time imaging and adaptive planning capabilities enhance safety by allowing clinicians to monitor and adjust treatment parameters as needed.
IGRT is used in the treatment of various types of cancer, including prostate, lung, breast, head and neck, and gastrointestinal cancers, among others. It represents a significant advancement in radiation therapy technology, allowing for personalized and effective cancer treatment while minimizing the risk of radiation-related complications.