SBRT (Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy)
Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT), also known as Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR), is an advanced form of radiation therapy that delivers highly precise and intense doses of radiation to small, well-defined tumors in the body. SBRT is typically used to treat tumors in the lungs, liver, spine, prostate, and other sites where surgery may not be feasible or when patients are not candidates for surgery.
Here's how SBRT works:
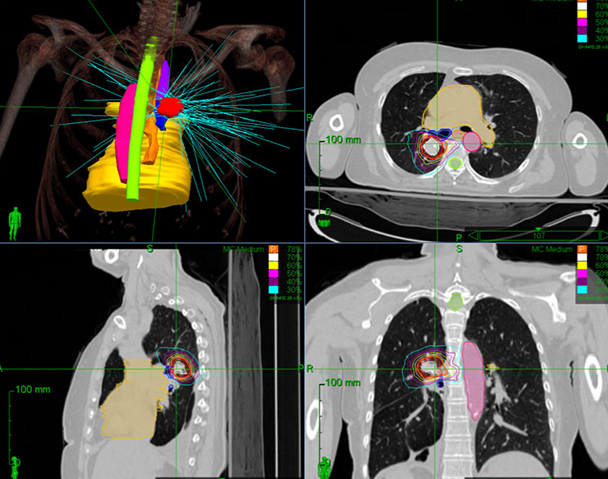
Precise Targeting: SBRT uses advanced imaging techniques such as CT scans, MRI, or cone-beam CT to precisely locate the tumor and map its position relative to surrounding structures. This high-resolution imaging allows radiation oncologists to accurately delineate the target volume and plan the delivery of radiation.
High-Dose Radiation: Unlike conventional radiation therapy, which delivers radiation in multiple fractions over several weeks, SBRT delivers a highly focused and intense dose of radiation in just a few treatment sessions. This high-dose approach is designed to effectively eradicate the tumor while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
Stereotactic Guidance: SBRT employs stereotactic principles to ensure precise delivery of radiation to the target volume. Stereotactic techniques involve using a coordinate system to accurately position the patient and align the radiation beams with the tumor, ensuring that the radiation is delivered with sub-millimeter accuracy.
Motion Management: SBRT is particularly effective for treating tumors that move with respiration or other bodily functions, such as lung tumors. Specialized techniques such as respiratory gating or tumor tracking are used to account for tumor motion and ensure accurate delivery of radiation, even as the patient breathes or moves.
Treatment Planning: Treatment planning for SBRT involves sophisticated computer algorithms that optimize the delivery of radiation based on the size, shape, and location of the tumor, as well as surrounding critical structures. The goal is to maximize tumor control while minimizing the risk of side effects.
Benefits of SBRT include:
High Treatment Efficacy: SBRT delivers a potent dose of radiation to the tumor, resulting in high rates of local tumor control and excellent clinical outcomes.
Shorter Treatment Course: SBRT typically requires only a few treatment sessions, often completed within a week, compared to conventional radiation therapy, which may span several weeks. This shortened treatment course offers greater convenience for patients and reduces the overall duration of treatment.
Minimal Damage to Surrounding Tissues: SBRT delivers radiation with sub-millimeter accuracy, sparing nearby healthy tissues and organs from unnecessary radiation exposure. This reduces the risk of side effects and complications associated with treatment.
Non-Invasive Alternative to Surgery: SBRT provides a non-invasive treatment option for patients who may not be candidates for surgery or prefer to avoid surgical intervention. It can be used to effectively treat tumors that are difficult to access surgically or located in sensitive areas of the body.
SBRT is widely used in the treatment of early-stage primary tumors, recurrent tumors, and metastatic lesions. It offers a safe, effective, and convenient treatment option for patients with localized cancer, providing excellent tumor control while minimizing the risk of treatment-related toxicity.